1. Explain morality etiquette and professional codes.
Morality
It is the human attempt to define what is right and wrong about our actions and thoughts, and what is good and bad about our being who we are.
- Ethics is the philosophy of morality. Therefore, morality means rightness or goodness.
- Morality is complex concept and philosophical beliefs by which an individual determines whether his actions are right or wrong
- People learn morals from parents, teachers, religious leaders, friends and experiences.
- Etiquette is a set of rules for well-mannered behavior.
- Etiquette is an unwritten code or rules of social or professional behavior
- If we violate the rules of etiquettes that we have read in the books then we rightly considered as ill-mannered, impolite or even uncivilized but not necessary immoral.
- But violation of etiquette can have moral implications.boss who calls to her female subordinates as “honey” or shows bad manners.
- Professional codes of ethics which are special rules governing the members of a profession, say of doctors, lawyers and so on.
- Rules like a lawyer has an uniform for the court without it, it is not entered in the court for the case.
2. Short note on ethics of Mahatma Gandhi.
Gandhi is considered as one of the greatest moral philosopher of India. The major principles of Gandhian ethics are:
- Ends and Means: Gandhi always emphasised on pure means and ends. Improper means cannot be adopted to achieve proper ends. As a wrong path cannot take you to right destination.
- Satyagraha: It is the continuous realisation for truth. It mainly includes self sacrifice, peace and non violence. Only a person with will and determination can follow satyagraha.
- Trusteeship: Wealthy people should acts Trustees of trust that looked after the welfare of the people.
- Concept of seven sins: Wealth without work, Pleasure without conscience, Knowledge without character, Commerce without morality, Science without Humanity, Religion without Sacrifice, Politics without Principle are seven sins in a society that should be rectified.
- Sarvodaya: It means Universal Upliftment of all. By inclusiveness many evils of the society can be removed.
- Dignity of Labor: Gandhi tried to established equality among all by making bread labor compulsory to all.
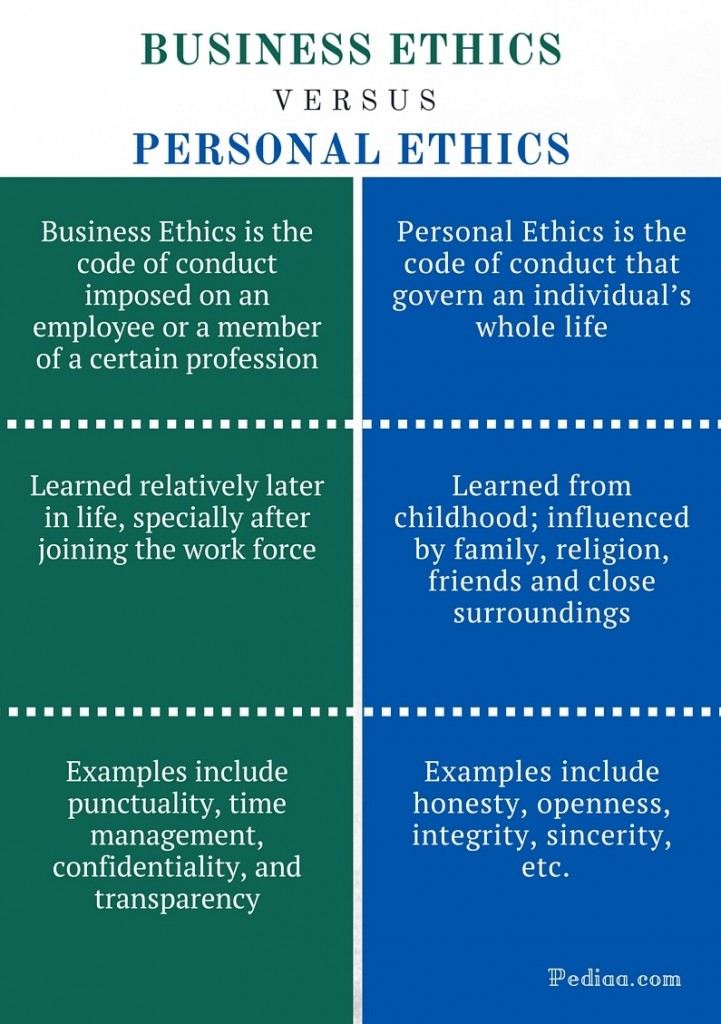
3. Differentiate Personal Ethics vs. Business Ethics.
The basic difference between the two is that personal ethics refers to a person's morals or values in any aspect of life. In contrast, business ethics refers to an individual's values within their work environment and how they conduct themselves professionally.
Here are the more differences between personal and business ethics:
Role-specificity: Sometimes, business ethics can differ depending on your role and industry. For instance, an accountant and a sailor might prioritize their values differently. However, your personal ethics remain the same regardless of your location or activity.
Structure: The structure of business ethics is usually organized and formalized as a mission statement. Personal ethics are usually flexible or informal.
Collective vs. individualized: The point to which groups of people share personal and business ethics can sometimes differ. This is because people can share personal ethics with a social group, family, or community, depending on how those groups develop the shared values. Business ethics refers to the standard procedures of an organization that all members must follow.
Situational nature: The types of values a person prioritizes often overlap between personal and business ethics. The fundamental difference is how they use them and in which situations they choose to apply them.
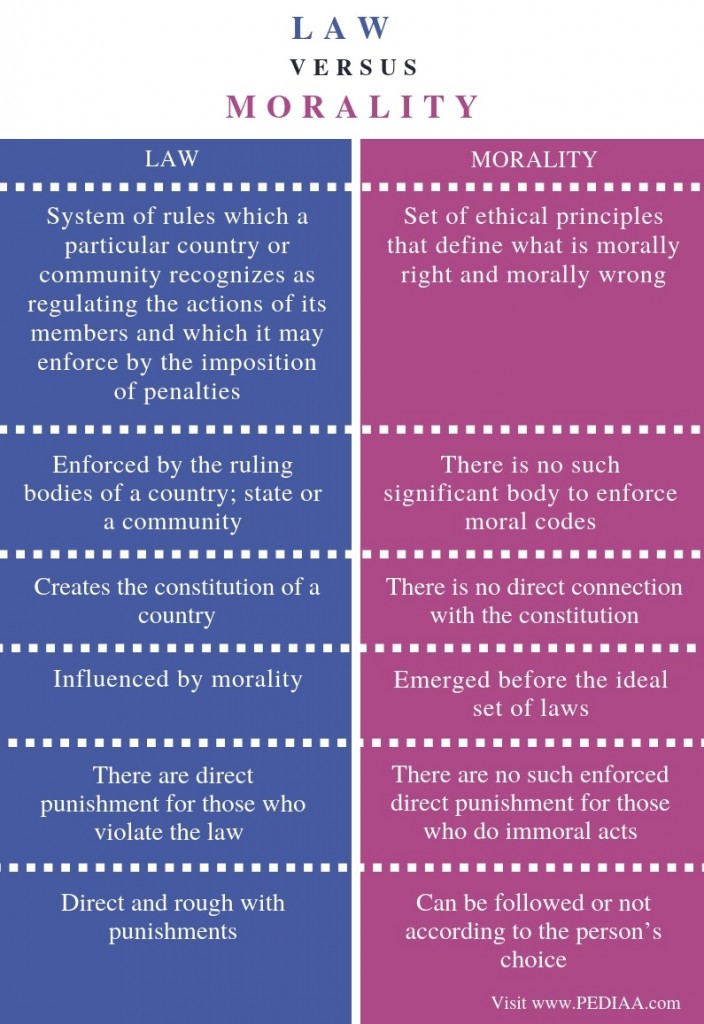
4. What is the difference between morality and law?
The main difference between law and morality is that law refers to the set of rules and regulations enforced by the state to regulate the human behavior in society whereas morality refers to the ethical code of conduct for a human being.
5. What factors influence the employee's decision making in business?
1 - Market Research. According to economist Rob Hyndman, to be successful, every business needs to be familiar with the market environment and this is why research is necessary in order to obtain necessary information.
For example, after exploring the market, the Taiwanese technology producer HTC incorporated the Android software in its mobile devices. This step boosted the sales of HTC products due to the high popularity of the Android operating system.
2 - Competition. Competition is another factor that strongly influences decision making processes within businesses. Since the market nowadays is highly competitive, business people always pay attention to the business operations of their rivals. For example, when Apple released its iPad tablet, Samsung quickly responded by releasing its Galaxy Tab which proves that while taking decisions on future developments, businesses consider competitors and their business development plans.
3 - Economic Environment. The Economic environment is particularly important because it is related to the buying capacity of customers and what products the people, in general, would afford. When taking decisions, business people bear in mind that they must comply with some standard and not, for instance, impose high prices on their production in times of financial recession. For example, Apple produces the iPhone mobile devices which are more expensive than similar devices by other brands. However, when major consumer states like the UK entered into severe financial crisis in the beginning of 2011, the company announced that it is developing a cheaper version of the iPhone that would respond to the economic environment in countries where there are financial problems.
4 - Social Responsibility. Social responsibility towards customers is also a factor that influences business decision making. Economist Paul Hohnen from the International Institute for Sustainable Development emphasizes that its concept is that business must be acting for the common good and in the interest of the general public. For example, UK legislation does not allow banks to impose unreasonably high fees on customers who are late with their mortgage payments. This legislation is followed by leading banking institutions in the UK such as HSBC and Lloyds TSB.
5 - Cost and Benefit. Financial expert April Dmytrenko highlights that for successful business decision making, it is required that business bodies create cost and benefit analysis. This approach takes into account expenses for the business from the process of production and revenue that would be generated when the product is put on sale. Thus business people are able to determine whether certain products would be a good business opportunity. For example, before releasing the Chevy Volt hybrid car, the business developers in Chevrolet analyzed a detailed cost and benefit plan. It determined that the revenue from Volt hybrid sales would justify the expenditures of its production.
6. Explain the following terms with respect to business: Loyalty, Reliability
Loyalty is the byproduct of a customer's positive experience with you and works to create trust. Loyal customers. Purchase repeatedly. Use what they purchase. Interact with you through a variety of different channels.
Customer loyalty is a result of a consistent satisfactory experience, which leads customers to favor one brand over the others. Loyal customers usually stay true to one brand because of the emotional bond that they create with it. These customers are usually the ones to buy high margin products and services.
7. How to apply moral philosophy to ethical decision making.
8. List and explain the roots of unethical behaviors.
Unethical behavior can be defined as actions that are against social norms or acts that are considered unacceptable to the public. Ethical behavior is the complete opposite of unethical behavior.
People often wonder why employees indulge in unethical practices such as lying, bribery, coercion, conflicting interest, etc. There are certain factors that make the employees think and act in unethical ways. Some of the influencing factors are ‘pressure to balance work and family, poor communications, poor leadership, long work hours, heavy work load, lack of management support, pressure to meet sales or profit goals, little or no recognition of achievements, company politics, personal financial worries, and insufficient resources’.
9. Explain various ethical modals that guide decision making.(Chapter 4)
10. What is an ethical dilemma? Give a suitable example.
An ethical dilemma involves the need to choose one option from am,, two or more morally acceptable courses of action. Here, one choice prevents selecting the other. Further there may also be a situation where we are forced to choose between equally unacceptable alternatives.
Ethics are the moral standards and principles by which entities (individuals and organizations) govern their behaviors and decision-making. When these standards and principles conflict with each other in a decision-making situation, an ethical dilemma may occur.
Some examples of ethical dilemma include:
- Taking credit for others’ work
- Offering a client a worse product for your own profit
- Utilizing inside knowledge for your own profit
11. Explain types of approach to resolve ethical dilemmas?
- Consider the option available (It includes finding and developing various options)
- Consider the sequences for each option (It can be positive or negative)
- Analyse actions
- Consider
- Decision making and commitment
- Evaluate the implemented decision
From Chapter 4 to 6
12. Explain concept of Ethical dilemmas.(Refer above two questions)
13. What values company expect from their employees?
14. Explain various ethical models that guide decision making.
15. What values company expect from their employees?
16. Explain Kohlberg's Model of Cognitive Moral Development.
17. Compare: Normative ethics and Applied ethics.
18. Give two examples of white collar crime.
19. How to apply moral philosophy to ethical decision making?
20. Explain honesty, integrity, transparency are the touchstones of business ethics.
21. Short note on ethics of Rabindranath Tagore.
22. Short note on ethics of Sri Aurobindo Ghose.
23. List the main pillars of Tagore's concept of education.
24. Write a brief note on the ethics and moral values of Swami Vivekananda.