DROP
DROP is used to delete a whole database or just a table.The DROP statement destroys the objects like an existing database, table, index, or view.
A DROP statement in SQL removes a component from a relational database management system (RDBMS).
Syntax:
DROP object object_name
Examples:
DROP TABLE table_name;
table_name: Name of the table to be deleted.
DROP DATABASE database_name;
database_name: Name of the database to be deleted.
TRUNCATE
TRUNCATE statement is a Data Definition Language (DDL) operation that is used to mark the extents of a table for deallocation (empty for reuse). The result of this operation quickly removes all data from a table, typically bypassing a number of integrity enforcing mechanisms. It was officially introduced in the SQL:2008 standard.
The TRUNCATE TABLE mytable statement is logically (though not physically) equivalent to the DELETE FROM mytable statement (without a WHERE clause).
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
table_name: Name of the table to be truncated.
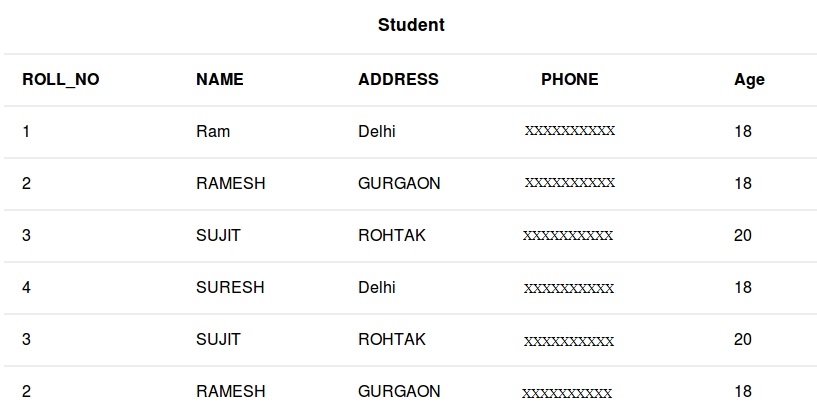
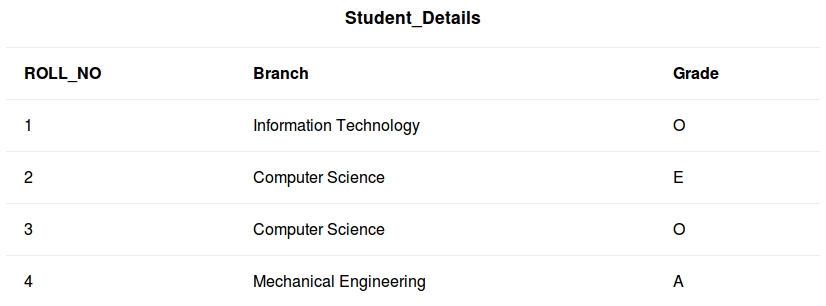
DATABASE name - student_data
DROP vs TRUNCATE
- Truncate is normally ultra-fast and its ideal for deleting data from a temporary table.
- Truncate preserves the structure of the table for future use, unlike drop table where the table is deleted with its full structure.
- Table or Database deletion using DROP statement cannot be rolled back, so it must be used wisely.
Queries
- To delete the whole database
DROP DATABASE student_data;After running the above query whole database will be deleted.
- To truncate Student_details table from student_data database.
TRUNCATE TABLE Student_details;After running the above query Student_details table will be truncated, i.e, the data will be deleted but the structure will remain in the memory for further operations