Summer 2021 Principles of Economics and Management (PEM) SEM 4 GTU Paper Solution :
- Production and Consumption of Goods and Services
- Supply (flow) of Money
- The Elasticity of Demand for a good is affected by its nature. Different goods can be a necessity good, a comfort good, or a luxury good for a person.
- There is one more thing that is a single good can be a necessity for one person, a comfort for the second person, and a luxury for a third person. So, we can say that a good’s nature is relative.
- Now, let us understand how nature affects the elasticity of demand.
- A necessity good like vegetables, food grains, medicines and drugs, has an inelastic demand. Such goods are required for human survival so their demand does not fluctuate much against a change in their price.
- A comfort good like a fan, refrigerator, washing machine, etc., has an elastic demand as their consumption can be postponed for a time period.
- A luxury good like AC, Cars, Diamond has a relatively high elasticity of demand when compared to comfort goods.
- The Price Elasticity of Demand for a good, with a large number of substitutes available, is very high.
- The possible reason behind this is that even a small rise in the price of such goods will induce its buyer to look for its substitutes. An example of this can be an FMCG product like a packet of chips. A rise of ₹2 on a packet of Lays will induce the buyer to go for Haldiram’s chips.
- Thus, the availability of a large number of close substitutes increases the sensitivity against change in price, or we can also say that this increases the Price Elasticity of Demand.
- The price level of goods plays a major role in determining the price elasticity of demand. Goods that fall in a higher price segment are more likely to have high elasticity.
- A price rise will further push them in the higher segment while even a small decline in the price can put them in the affordable segment. An example of this can be mobile phones or laptops. A person with a budget of 15k won’t go for a phone that is 20% more costly.
- On the other hand, goods that belong to the low-price segment are generally inelastic or relatively less elastic. An example can be a packet of matchboxes. Even a sharp rise in its price won’t throw it into the high-price segment.
- Our society is divided into different classes based on incomes and lifestyle. Upper-class people generally have a higher income and live a lavish life whereas the lower class people can’t afford luxury items because they have a low income.
- Income levels have a considerable effect on the elasticity of demand. The Elasticity of Demand for a commodity is generally very low for higher income level groups. The change in prices does not bother people from such groups.
- Whereas the Price Elasticity of Demand of a commodity is very high for people belonging to low-income level groups. Poor people are highly affected by the change in the prices of commodities.
- The price elasticity of demand varies directly with the time period. The given time period can be as shorts as a day and as long as several years.
- The price elasticity of demand is directly proportional to the time period. This means the elasticity for a shorter time period is always low or it can be even inelastic.
- The reason stated for this is the redundant human nature to change habits. We generally stick to a commodity and respond very late to the price changes. However, the elasticity of demand is high in a longer time period as our habit changes over time. We can substitute the original product if its price changes in the long run.
- These were the factors that affect the Price Elasticity of Demand. Let us now sum up the blog by looking at the key takeaways.

| Basis of Difference | Perfect Competition | Monopoly |
| Meaning | It refers to the market in which there are many firms selling a certain homogenous product. | A monopoly market is a market structure in which a single firm is a sole producer of a product for which there are no close substitutes available in the market |
Output | Price is equal to the marginal cost at the equilibrium output. | Price is greater than the average cost at equilibrium output. |
| Equilibrium | It is possible only when MR=MC and MC cut the MR curve from below. | Equilibrium can be realized whether the MC is rising, constant, or falling. |
Barriers for entry of new firms | Here, there are no restrictions or barriers for new firms to enter the market. | It has strong restrictions for the entry of new firms into the market. |
Price Discrimination | There is no price discrimination by sellers as the prices are determined by supply and demand forces. | The monopolist can charge different prices from different groups of buyers. |
Supply Curve | Here, the supply curve can be identified as all firms sell the desired quantity at the prevailing price. | In a monopoly, the supply curve cannot be known because of price discrimination. |
Control over Price | Here, the sellers don’t have any control over the price. | In this market, the seller has full control over the price. |
Sellers are known as | In this market, the sellers are known as price takers. | In this market, the sellers are price makers. |
Degree of Competition | This market has strong competition in the market. | There is no competition in the market. |
Close Substitutes | In this market, close substitutes are available. | There are no close substitutes for the products in this market. |
Number of sellers | There are a large number of sellers with a large number of Buyers offering homogenous products. | There is only one single seller of a commodity with a large number of buyers. |
- A cow. Cattle have been used as money at different points in history.
- A stack of U.S. 20-dollar bills equal to the value of one cow.
It is a financial tool that is used by the central banks in regulating the flow of money and the interest rates in an economy | It is a financial tool that is used by the central government in managing tax revenues and policies related to expenditure for the benefit of the economy |
Central Bank of an economy | Ministry of Finance of an economy |
It measures the interest rates applicable for lending money in the economy | It measures the capital expenditure and taxes of an economy |
Stability of an economy | Growth of an economy |
Exchange rates improve when there is higher interest rates | It has no impact on the exchange rates |
Monetary policy targets inflation in an economy | Fiscal policy does not have any specific target |
Monetary policy has an impact on the borrowing in an economy | Fiscal policy has an impact on the budget deficit |
| Basic Terms | Management | Administration |
| Meaning | It is the skill of organizing people, resources and getting work done | It is the process of setting up objectives and crucial policies |
| Authority | Both middle and lower level | Strictly upper level |
| Core function | Policy implementation | Policy formulation |
| Role | Executive | Decisive |
| Area of Operation | Work under administration | Fully control over activities |
| Key Person | Manager | Administrator |
| Function | Governing and executive | Legislative and determinative |
| Main Focus | Managing work | Making policies and assembling resources |
| Application | Profit-making organizations | Government offices, business enterprises, military, religious, hospitals, clubs, and educational organizations. |
| Decides on | Who will do the work? And How will it be done? | What should be done? And when should it be done? |
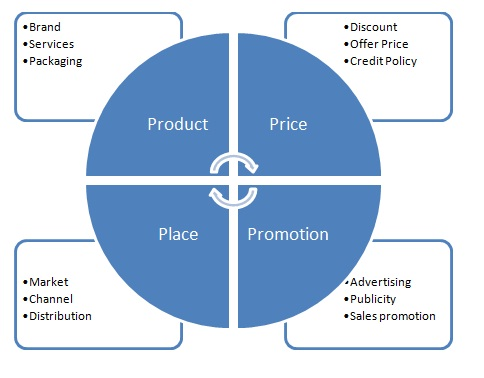
- Product: What you sell. Could be a physical good, services, consulting, etc.
- Price: How much do you charge and how does that impact how your customers view your brand?
- Place: Where do you promote your product or service? Where do your ideal customers go to find information about your industry?
- Promotion: How do your customers find out about you? What strategies do you use, and are they effective?
Importance of HR managers in organisations
- Strategy management: This is an important aspect of any organisation and plays a vital role in human resource management. HR managers manage strategies to ensure the organisation reaches its business goals, as well as contributing significantly to the corporate decision-making process, which includes assessments for current employees and predictions for future ones based on business demands.
- Benefits analysis: HR managers work towards reducing costs, such as with recruitment and retention. HR professionals are trained to conduct efficient negotiations with potential and existing employees, as well as being well-versed with employee benefits that are likely to attract quality candidates and retaining the existing workforce.
- Training and development: Since HR managers contribute significantly to training and development programmes, they also play a pivotal role in strengthening employer-employee relationships. This contributes to the growth of employees within the company, hence enhancing employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Interactivity within employees: HR managers are responsible for conducting activities, events and celebrations in the organisation which gives way to team building opportunities. Moreover, it enhances interactivity within employees and instils a sense of trust and respect among peers.
- Conflict management: The department to go to when any kind of professional conflict arises between employees is HR. They ensure that issues and conflicts are resolved effectively, approaching the problem with an unbiased attitude and encouraging effective communication to reach a solution. In addition, they help employees understand various ways of developing effective work relationships and the importance of not letting personal judgement affect their behaviour.
- Establishing a healthy work culture: A healthy work culture is pivotal in bringing out the best in employees. HR managers contribute significantly in setting up a healthy and friendly work culture, which further translates into better productivity among employees.
- Compliance: HR professionals work towards making the organisation compliant with employment laws, as well as maintaining records of hiring processes and applicants’ log.
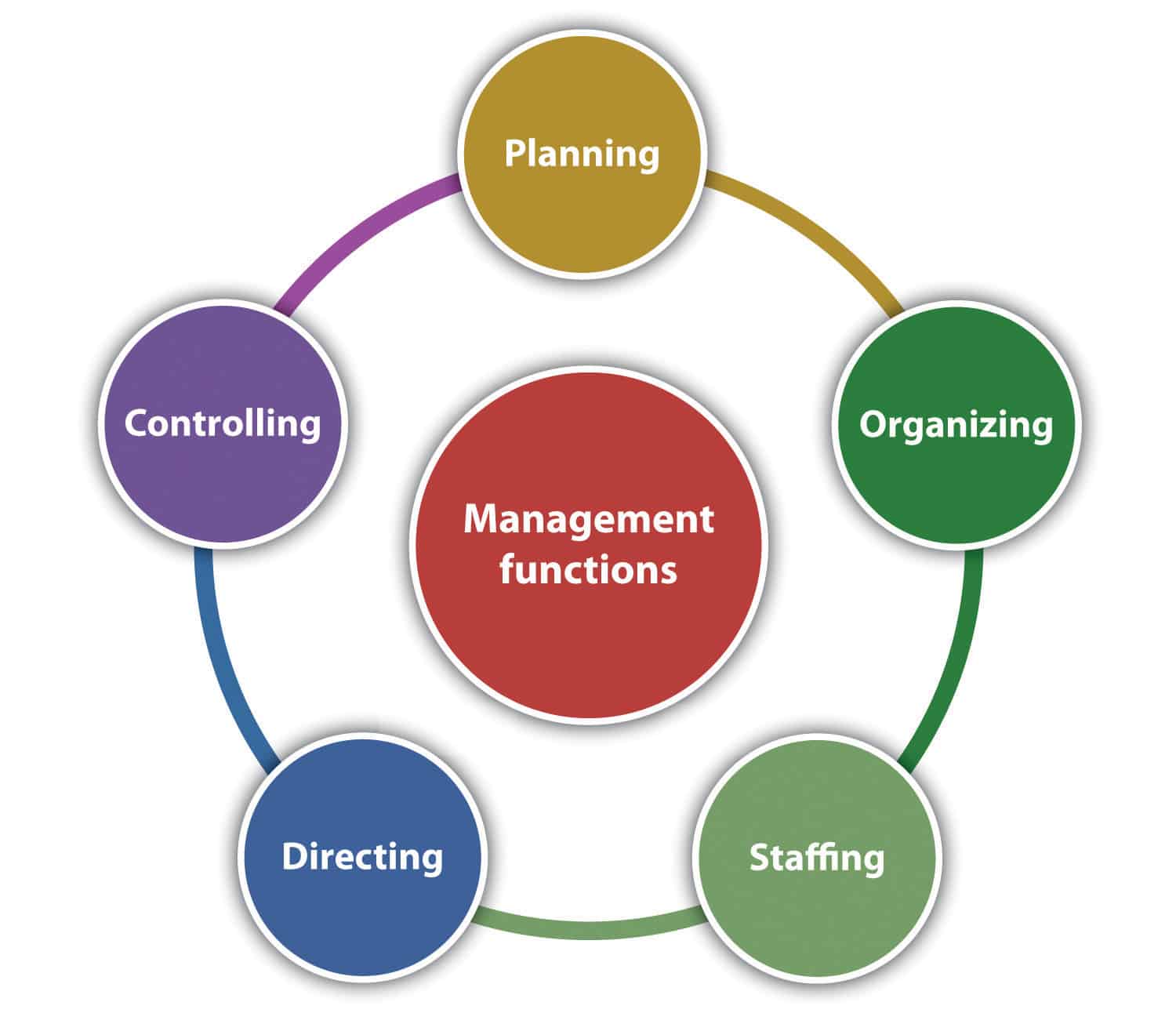
- Maintain the day-to-day operation of a department or function
- Represent the planning, organizing, staffing, and controlling that are needed to achieve a goal or produce an output
- Deal with creating a vision and strategic direction of an organization, or group of people
- Establish a culture and create conditions that facilitate the journey
- CSR increases employee engagement
- CSR improves bottom-line financials
- CSR supports local and global communities
- Contributes to the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals
- Increases investment opportunities
- Presents press opportunities
- Increases customer retention and loyalty
- CSR improves employer branding
Internal Sources
Internal sources of recruitment refers to the recruitment of employees who are already a part of the existing payroll of the organisation. The vacancy for the position can be informed to the employee through internal communication.
There are different types of internal hiring in the organisation and they are as follows:
1. Promotion: Promotion is referred to as the change of designation of the employee. It involves shifting of the existing employee to a higher position within the organisation and providing that employee with more responsibility and a raise in pay.
Promotion helps in motivating the other employees of the organisation to work hard so that they also become eligible for promotion.
2. Transfer: Transfer refers to the shifting of an existing employee from one department to another department in an organisation.
3. Employee Referrals: It can happen that the organisation in an effort to cut down costs on hiring is looking for employee referral. The employees are well aware of the job roles in the organisation for which manpower is required. These employees will refer potential candidates by screening them based on their suitability to the position.
4. Former employees: Some organisations have the provision of hiring retired employees willing to work part time/full time for the organisation.
Advantages of Internal Sources
Following are the advantages of the internal sources:
1. The organisation saves money on hiring programmes which translates to higher revenue for business.
2. It makes selection and transfer of employees very easy.
3. Internal source of recruitment serves as a morale booster for the existing employees.
4. It provides a sense of loyalty towards the business which results in improved productivity.
5. As existing employees will be aware of the working pattern of the organisation, therefore it will take much less time for the re-hires to get adapted to working conditions.
Disadvantages of Internal Sources
Following are some of the disadvantages of the internal sources:
1. Internal recruitment causes reduction in the morale of those employees who are not selected or considered for appraisal.
2. It discourages capable persons from outside to join to work in the company.
3. It can lead to conflict if one employee is selected for promotion, while the others are not considered.
External Sources
External sources of recruitment seek to employ candidates that have not been recruited anytime before in the organisation.
Introduction of fresh talent among the workforce leads to growth and development of the business.
Following are the some of the external sources of recruitment:
1. Advertisement: Advertisements serve as a great source of information regarding any job opportunities. This type of source is used for recruitment of middle level employees, or high level employees.
2. Employment Exchanges: Employment exchanges serve as a source of recruitment for the people as it is run by the government.
3. Employment portals: In this age of technology, development in the field of hiring has taken place. Nowadays many employment portals are open where one can find information about job openings.
4. Educational Institutions: Educational institutions also serve as a good source of recruitment as many students or say resources will be available at once under one roof.
5. Recommendation: This can also be a good source of recruitment as an existing employee will be able to provide better recommendation for other candidates.
Advantages of External Source
Following are some of the advantages of external sources.
1. It helps in availability of proper skilled labour.
2. There will be availability of new ideas from employees hired using external sources.
3. The employees join as knowledgeable persons which reduces the training time required for new hires.
Disadvantages of External Source
1. It can lead to unhappy employees as the existing employees may feel that they deserved an opportunity for growth.
2. It can lead to lack of cooperation between the new hires and the existing employees.
3. It is a lengthy process where the employee needs to appear for many rounds.
For More :
[SEM 4] Computer Engineering GTU Paper
Solution | GTU Medium: Click
Here
GTU Study Materials | GTU Medium: Click Here
GTU IMP & Question Banks | Bachelor
of Engineering | GTU Medium: Click
Here
GTU Old Papers | Bachelor of Engineering | GTU Medium: Click
Here
Note: If Telegram link not works then go and
search GTU medium in Telegram App.



-Logo.wine.png)